| CaF2 (Calcium Fluoride) crystal is not only
a conventional but also an excellent material for the applications of
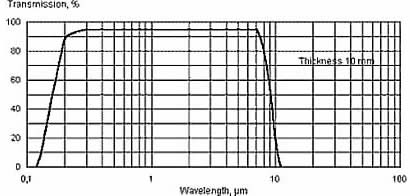
laser optics. The crystal covers a very wide transmission range from 130nm
to 9500 nm (UV, VIS and IR), especially, features a high transmittivity
in IR range. Those advantages make CaF2 an ideal material widely
used in Laser, IR and UV optics for making optical windows and lenses,
etc.

Main Properties:
| Formula |
CaF2 |
| Structure |
Cubic |
| Growth Method |
Stockbarger Technique |
| Maximum Size |
¦µ180 mm |
| Transmission Range (¦Ìm) |
0.15 - 9.0 |
| Density (g/cm3) |
3.18 |
| Melting point (¡ãC) |
1418 |
| Hardness (Mohs) |
4 |
| Thermal Expansion Coefficient (10-6/K) |
16.2-19.4 |
| Thermal Conductivity(W m-1K-1) |
9.17 |
| Specific Heat Capacity (J kg-1K-1) |
888 |
| Solubility in Water (g/100 cm3) |
0.0016 |
| Solubility in Acids |
unessential |
| Solubility in Organic Solvents |
insoluble in acetone |
Wavelength (¦Ìm)
Refractive Index |
0.2 |
0.5 |
1.0 |
5.0 |
10.0 |
12.0 |
1.4951 |
1.4365 |
1.4289 |
1.3990 |
1.3002 |
1.2299 |
|
| Absorption Coefficient (cm-1) |
0.10 at 0.2 ¦Ìm
0.01 at 0.4 ¦Ìm
0.03 at 2.6 -2.9 ¦Ìm |
Transmission Spectrum: (Thickness 10 mm)
|

